Abstract
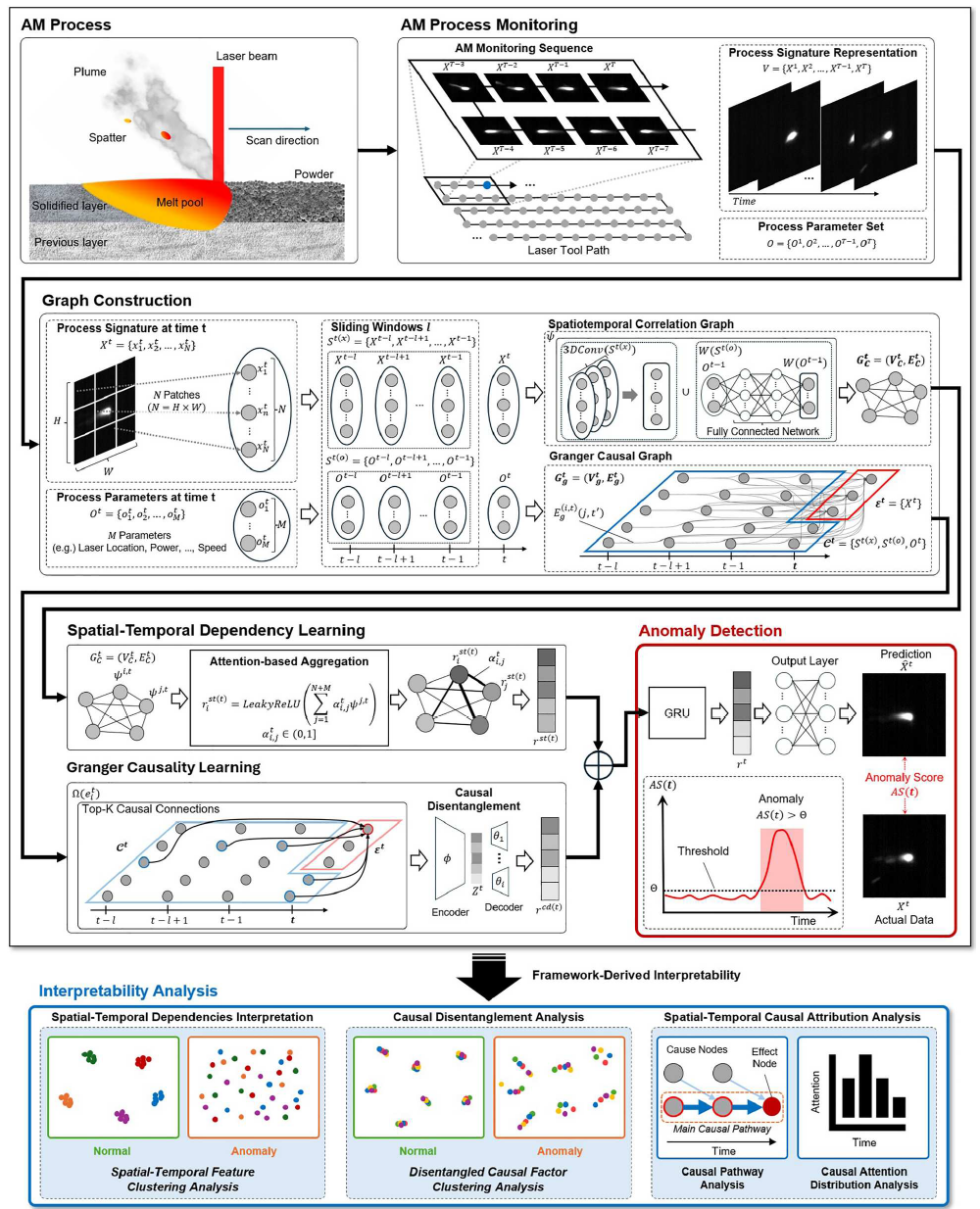
In additive manufacturing (AM) processes, in-situ monitoring combined with machine learning (ML) approaches plays a crucial role in ensuring consistent product quality and preventing defects. However, existing ML methods for anomaly detection predominantly rely on correlation-based models that lack interpretability and fail to capture underlying spatiotemporal and causal dynamics. This study proposes an anomaly detection framework that integrates spatiotemporal dependency learning (STL) and Granger causality learning (GCL) through graph attention network mechanisms. The STL module enforces spatial consistency and temporal smoothness in learned feature representations, while the GCL module identifies causal relationships between historical process signatures and both historical and current parameters, and current states through attention-based causal aggregation and disentanglement techniques. By combining these complementary modules, our method achieves superior anomaly detection performance while providing interpretable insights through spatial-temporal dependency interpretation, causal disentanglement analysis, and causal attribution analysis. Experimental validation demonstrates improved detection accuracy compared to existing baselines, with attention-based mechanisms enabling the identification of specific process parameters and spatial regions contributing to anomalous behaviour. This framework facilitates proactive quality control in AM processes by bridging the gap between high-accuracy anomaly detection and practical interpretability requirements in manufacturing applications.